S&P Global Pushes Back Fed Rate Cut Expectations

Sign up for Global Macro Playbook: Stay ahead of the curve on global macro trends.
S&P Global has revised its forecast for the Federal Reserve's interest rate path, delaying the anticipated timing of the first rate cut to December 2024. This shift in expectations, driven by persistent inflation exceeding the Fed's target, could have significant spillover effects on global economies, particularly in Europe.
The revised forecast now anticipates a cumulative 250 basis points of rate cuts, with the terminal policy rate expected to be reached in the second half of 2026. This delay in US monetary policy easing raises concerns about potential impacts on other central banks' decisions and global financial conditions.
While S&P Global believes that most European central banks will likely proceed with their planned rate cuts as scheduled, the report acknowledges the potential for indirect influence from the Fed's revised timeline. The Bank of England (BoE), in particular, might adopt a more cautious approach to rate cuts in 2025, depending on developments in the UK labor market and domestic inflation pressures.
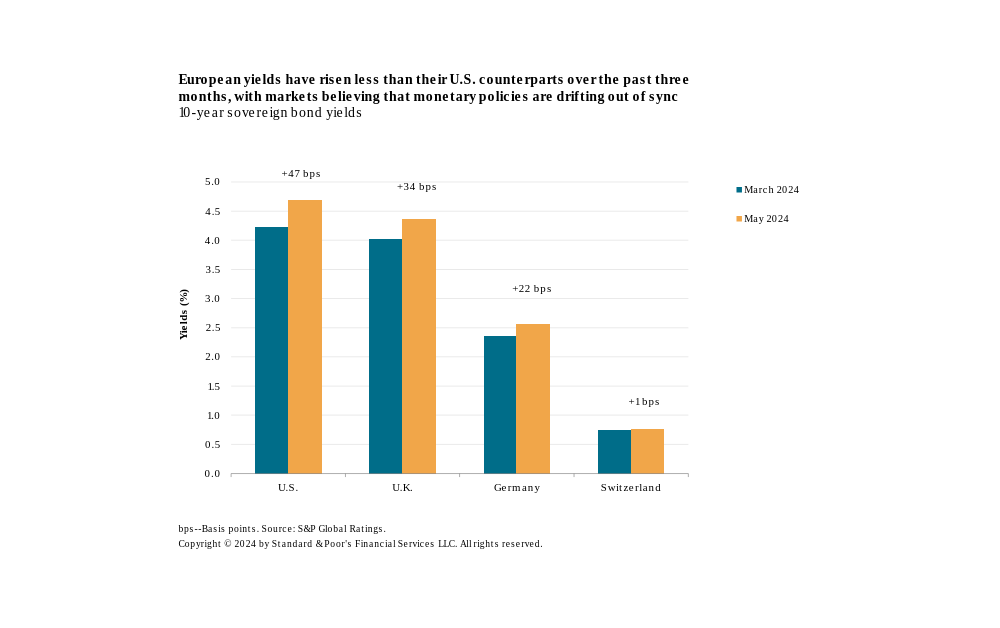
S&P Global's report also highlights two key channels through which US monetary policy influences European economies: exchange rates and financial conditions.
Exchange Rate Channel: When US interest rates rise relative to European rates, European currencies tend to depreciate against the US dollar. This depreciation can have both inflationary and stimulative effects. On the one hand, it can contribute to inflation by raising the cost of imported goods, particularly energy, as Europe relies heavily on energy imports. On the other hand, a weaker currency can boost exports by making European goods more competitive in international markets. While the inflationary impact often dominates in the short term, leading to a contractionary effect on GDP, this effect can be mitigated or even reversed in the medium term if the depreciation is sustained and leads to a significant increase in exports.
Financial Conditions Channel: Beyond exchange rate fluctuations, US interest rates also exert influence through their impact on financial conditions in Europe. When US long-term interest rates rise relative to European rates, it can incentivize European investors to shift their savings towards US assets, seeking higher returns. This outflow of capital can put upward pressure on European long-term interest rates, tightening financial conditions and potentially impacting economic activity.
"Central banks in Europe will probably seek to communicate with the markets to shield the European curve from potential rises in U.S. long-term yields," S&P Global points out. "Against this backdrop, the Fed's announcement that it will slow the pace of reductions in holdings of U.S. Treasuries from June onwards is a factor mitigating the risk of an unwarranted tightening of financing conditions in Europe."